
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug Regimen
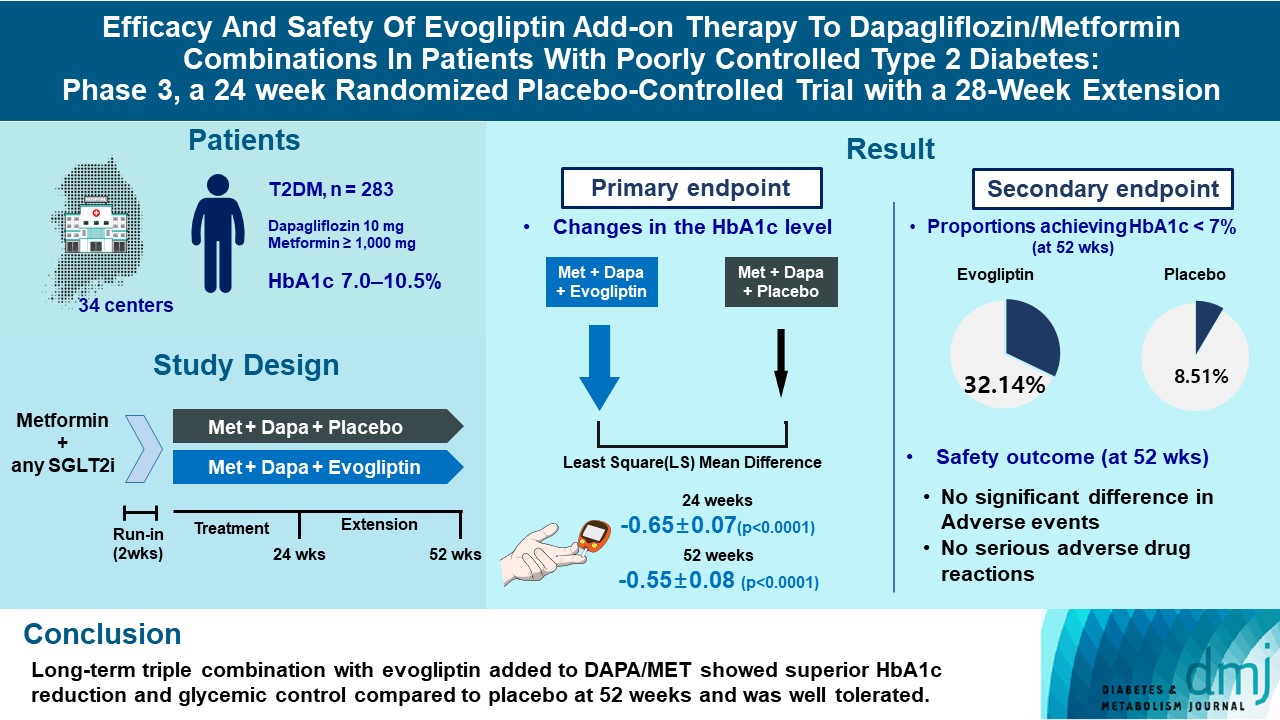
- Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extension
- Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):808-817. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0387
- 2,754 View
- 290 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigates the long-term efficacy and safety of evogliptin add-on therapy in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) previously received dapagliflozin and metformin (DAPA/MET) combination.
Methods
In this multicenter randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels 7.0% to 10.5% (n=283) previously used DAPA 10 mg plus MET (≥1,000 mg) were randomly assigned to the evogliptin 5 mg once daily or placebo group (1:1). The primary endpoint was the difference in the HbA1c level from baseline at week 24, and exploratory endpoints included the efficacy and safety of evogliptin over 52 weeks (trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04170998).
Results
Evogliptin add-on to DAPA/MET therapy was superior in HbA1c reduction compared to placebo at weeks 24 and 52 (least square [LS] mean difference, –0.65% and –0.55%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.79 to –0.51 and –0.71 to –0.39; P<0.0001). The proportion of patients achieving HbA1c <7% was higher in the triple combination group at week 52 (32.14% vs. 8.51% in placebo; odds ratio, 5.62; P<0.0001). Evogliptin significantly reduced the fasting glucose levels and mean daily glucose levels with improvement in homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function (LS mean difference, 9.04; 95% CI, 1.86 to 16.21; P=0.0138). Adverse events were similar between the groups, and no serious adverse drug reactions were reported in the evogliptin group.
Conclusion
Long-term triple combination with evogliptin added to DAPA/MET showed superior HbA1c reduction and glycemic control compared to placebo at 52 weeks and was well tolerated.
- Risk Factors Associated with Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetic Patients without Hypertension
- Jung Hyun Noh, Joon Hyung Doh, Sung Yun Lee, Tae Nyun Kim, Hyuk Lee, Hwa Young Song, Jeong Hyun Park, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong Jun Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(1):40-46. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.1.40
- 4,639 View
- 38 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Hypertension and age are recognized as important risk factors for left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction. Some studies have shown that diabetes itself may also be an independent risk factor for LV diastolic dysfunction, although this is controversial. The aim of this study was to determine the factors associated with LV diastolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes in the absence of hypertension or ischemic heart disease (IHD).
Methods Participants in this study consisted of 65 type 2 diabetes patients (M : F = 45 : 20; mean age 51 [26 to 76] years; mean body mass index [BMI] 25.0 ± 2.5 kg/m2) without hypertension, heart disease, or renal disease. Individuals with ischemic electrocardiographic changes were excluded. LV diastolic function was evaluated by Doppler echocardiographic studies.
Results Fifteen patients (23.1%) showed LV diastolic dysfunction on Doppler echocardiographic studies. Patients with LV diastolic dysfunction were older than those without diastolic dysfunction (60.0 ± 2.5 vs. 50.5 ± 1.9 years;
P < 0.01). After adjusting for age and sex, BMI was higher (26.6 ± 0.7 vs. 24.6 ± 0.3 kg/m2;P < 0.01) and diabetes duration was longer (9.65 ± 1.48 vs. 4.71 ± 0.78 years;P < 0.01) in patients with LV diastolic dysfunction than in those without diastolic dysfunction. There were no differences in sex, smoking, blood pressure, lipid profiles, hemoglobin A1C, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, or diabetic microvascular complications between the LV diastolic dysfunction group and the normal diastolic function group. After adjusting for age, sex, and BMI, diabetes duration was found to be independently associated with LV diastolic dysfunction (odds ratio 1.38; confidence interval 1.12 to 1.72;P = 0.003).Conclusion These results suggest that diabetes duration may be a risk factor for LV diastolic dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients without hypertension or IHD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reducing Cardiac Steatosis: Interventions to Improve Diastolic Function: A Narrative Review
Kiyan Heshmat-Ghahdarijani, Roya Modaresi, Sobhan Pourmasjedi, Setayesh Sotoudehnia Korani, Ali Rezazadeh Roudkoli, Razieh Ziaei, Armita Farid, Mehrnaz Salehi, Afshin Heidari, Sina Neshat
Current Problems in Cardiology.2023; 48(8): 101739. CrossRef - Glycemic variability is associated with diastolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes
Yana Dzhun, Georgy Mankovsky, Nadiya Rudenko, Yevgen Marushko, Yanina Saienko, Borys Mankovsky
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108519. CrossRef - Lipids and diastolic dysfunction: Recent evidence and findings
Padideh Daneii, Sina Neshat, Monir Sadat Mirnasiry, Zahra Moghimi, Fatemeh Dehghan Niri, Armita Farid, Setayesh Sotoudehnia Korani, Masood Shekarchizadeh, Kiyan Heshmat-Ghahdarijani
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(6): 1343. CrossRef - Does diabetes increase the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with negative treadmill stress echocardiography?
So Young Yang, Hui-Jeong Hwang
Endocrine Journal.2022; 69(7): 785. CrossRef - Factors associated with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with septic shock
Wei-Dong Ge, Feng-Zhi Li, Bang-Chuan Hu, Li-Hong Wang, Ding-Yuan Ren
European Journal of Medical Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - An in-depth analysis of glycosylated haemoglobin level, body mass index and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes
Xin Zuo, Xueting Liu, Runtian Chen, Huiting Ou, Jiabao Lai, Youming Zhang, Dewen Yan
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Early detection of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction using conventional and speckle tracking echocardiography in a large animal model of metabolic dysfunction
Mark M. P. van den Dorpel, Ilkka Heinonen, Sanne M. Snelder, Hendrik J. Vos, Oana Sorop, Ron T. van Domburg, Daphne Merkus, Dirk J. Duncker, Bas M. van Dalen
The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Factors Associated with Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetic Patients without Hypertension (Korean Diabetes J 2010;34:40-6)
Dong-Lim Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(2): 135. CrossRef
- Reducing Cardiac Steatosis: Interventions to Improve Diastolic Function: A Narrative Review
- Serum Adiponectin, TNF-alpha, IL-6 and Insulin Resistance in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Young A Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Dong Jun Kim, Tae Hyun Um, Chong Rae Cho, Na young Jang, Soo Kyung Kwon, Soon Hee Lee, Jeong Hyun Park, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Kyung Ho Lim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(2):104-111. Published online March 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.2.104
- 2,567 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
To determine plasma adipokines such as adiponectin, IL-6 and TNF-alpha concentrations in women with and without polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and to assess possible correlations of adipocytokines to the hormonal and metabolic parameters, including measures of insulin resistance (IR). METHODS: Forty-four selected women were classified as follows: 13 obese (body mass index [BMI] > or = 25 kg/m(2)) with PCOS; 15 non-obese (BMI < 25 kg/m(2)) with PCOS; 8 obese without PCOS, and 8 non-obese without PCOS. Blood samples were collected from all women with or without PCOS after an overnight fast. Serum levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), total testosterone, 17-alpha-hydroxyprogesterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), insulin, glucose, adiponectin, TNF-alpha and IL-6 were measured. Measures of IR included HOMA-IR and QUICKI. RESULTS: In non-obese group, fasting insulin levels and HOMA-IR in PCOS were significantly higher compared to control. However, Adiponectin, TNF-alpha and IL-6 concentrations were found not to be different in obese women with PCOS as compared with obese women without PCOS and in non-obese women with PCOS as compared with non-obese women without PCOS. Adiponectin concentrations correlated inversely with BMI, waist circumference (WC), total fat mass, serum insulin, and HOMA-IR in PCOS group. However, multiple regression analysis showed that BMI was the only independent determinant of adiponectin concentration. CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that insulin sensitivity per se probably does not play any role in the control of adipokines levels such as adiponectin, TNF-alpha and IL-6 in PCOS women -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adiponectin in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Hyun-Young Shin, Duk-Chul Lee, Ji-Won Lee
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2011; 32(4): 243. CrossRef
- Adiponectin in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- Insulin Secretory Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans: A Minimal Model Analysis.
- Sung Hoon Kim, Dong Jun Kim, Byung Wan Lee, In Ah Seo, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Moon Kyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(5):414-419. Published online October 1, 2003
- 1,411 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Type 2 diabetes is a complex, heterogeneous disorder, characterized by impairments in both insulin secretion and insulin action. This study was done to examine the significance of alterations in insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in Korean subjects with varying degrees of glucose intolerance. METHODS: Forty Korean subjects were studied, 12 with normal glucose tolerance (NGT), 14 with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and 14 with type 2 diabetes. An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed on each subject. Insulin sensitivity (SI), glucose effectiveness (Sg), acute insulin response after intravenous glucose (AIRg) and the disposition index (DI= SI x AIRg) were measured by the insulin-modified, frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test (FSIGT). RESULTS: Neither fasting serum insulin level nor SI was significantly different among the NGT, lGT and diabetes groups. Sg was significantly lower in the type 2 diabetes group than in the NGT group. The mean AIRg was blunted in the IGT and diabetes groups when compared with the NGT group. DI was more powerful in differentiating between NGT and IGT, compared to AIRg alone. CONCLUSION: These findings suggest that a defect in the compensatory insulin secretion might be more important than insulin resistance in the development of type 2 diabetes in Korean subjects.
- The Prevalence of Islet Cell Cytoplasmic Antibody in Korean Type 1 Diabetes: Possible Replacement with Combined Measurement of Anti-GAD, Anti-ICA512, and Anti-phogrin Antibodies.
- Kyoung Ah Kim, Dong Jun Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Yong Ki Min, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Dong Kyu Jin, Kyung Soo Ko, Sang Jin Kim, Myung Shik Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2001;25(6):430-445. Published online December 1, 2001
- 1,424 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Type 1 diabetes includes all forms of autoimmune-mediated and idiopathic beta-cell destruction leading to an absolute insulin deficiency. Evidence of an autoimmune pathogenesis was assessed by studying cytoplasmic islet cell antibodies (ICA), antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase (GADA), antibodies reacting with an islet tyrosine phosphatase-related molecule referred to as ICA512 (ICA512A), or its homologue phogrin (phogrin-A). In comparison with ICA, the best validation to assess the risk of type 1 diabetes, shows that a combination of antibodies to GADA with ICA512A has the power to detect a majority of ICA and 97~100% of subjects who progressed to overt diabetes. These findings suggest the possibility of replacing the laborious ICA test in the screening programs to identify subjects at risk of progressing to type 1 diabetes or forclassifying the stage of diabetes at the time of diagnosis. Up to now, it is unclear whether these results are applicable to the slowly progressive type 1 diabetes that appears to be more prevalent in Asian than in western countries. The prevalence of combined autoantibody testing (1 of GADA, ICA512A, or phogrin-A) was investigated in the patients with type 1 diabetes (typical and slowly progressive) and type 2 diabetes, and compared with that of ICA which is a more laborious and insensitive test. METHODS: The ICA assay was performed using immunoenzymatic staining of frozen human (blood group O) pancreatic sections with serial dilutions of serum samples with peroxidase-labeled protein A. For the GADA determination, commercially available GADA radioimmunoassay kits utilizing the 125I-labeled recombinant GAD65 (RSR , United Kingdom) as an antigen was used. Either ICA512A or phogrin-A were detected by a radioligand-binding assay after in vitro transcription and translation using the clone ICA512bdc or phogrin cDNA. Serum was obtainedfrom 76 patients with type 1 diabetes (mean age 22.8+/-14.0 years), 22 patients with slowly progressive type 1 diabetes (mean age 37.9+/-13.9 years) and 39 patients with type 2 diabetes (mean age 45.3+/-12.3 years). Typical and slowly progressive type 1 diabetes patients had the disease for between 4.0+/-4.6 and 10.1+/-9.5 years, respectively at the earliest serum sampling. RESULTS: 1) In typical type 1 diabetes, 30% of patients tested positive for ICA and 57% for the combined autoantibody test (1 of GADA, ICA512A, or phogrin-A). In the slowly progressive type 1 diabetes group, 18% of patients tested positive for ICA and 50% for the combined autoantibody test. In type 2 diabetes, 7.7% and 5.1% tested positive, respectively. 2) Ninety-six percent of ICA-positive patients expressed one or more of the 3 auto-antibody specificities in typical type 1 diabetes. Among the 53 ICA-negative patients with typical type 1 diabetes, 40% had one or more of these auto-antibodies. In the slowly progressive type 1 diabetes, 100% of the ICA-positive and 39% of the ICA- negative patients expressed one or more of the 3 autoantibody specificities. 3) Of the 23 patients with ICA-positive typical type 1 diabetes patients, 87% had a positive result for GADA, 48% for ICA512A, 44% for phogrin-A, and 96% for GADA or ICA512A. Of the 4 patients with ICA-positive slowly progressive type 1 diabetes, three had a positive result for GADA, and 1 for ICA512A. 4) When the prevalence of combined autoantibody testing was analyzed according to the duration of diabetes, the prevalence in patients tested within 4 years after the diagnosis and more than 4 years after the diagnosis was 61% and 52%, respectively in typical type 1 diabetes. Furthermore, that for the ICA was 37% and 21%, respectively. In the slowly progressive type 1 diabetes, the prevalence of combined auto-antibody testing was 88% and 25%, respectively (p<0.05), while that of ICA was 25% and 13%, respectively. 5) In typical type 1 diabetes, ICA were detected more frequently in patients younger than 15 years of age (48%) than in older patients (23%) (p<0.05), while the prevalence of combined auto-antibody testing -was not different according to the onset age (65% vs 53%). CONCLUSION: Combined autoantibody testing for GADA and ICA512A is more sensitive that ICA in type 1 diabetes. Therefore, it could replace the laborious ICA measurement and may be useful for discriminating the etiology of adult onset atypical diabetes.
- Insulin Secretion and Insulin Sensitivity in Korean Subjects with Impaired Glucose Intolerance.
- Dong Jun Kim, Jong Ryul Hahm, In Kyoung Jeong, Tae Young Yang, Eun Young Oh, Yoon Ho Choi, Jae Hoon Chung, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2000;24(3):356-364. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,343 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Although insulin resistance has been known to be a primary defect causing type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians and Caucasians. However, insulin secretory defect rather than insulin resistance has been speculated and demonstrated to be a more important factor in the development of type 2 diabetes in other ethnic groups. Thus, we undertook this study to investigate the initial abnormality of glucose intolerance in Korean subjects. METHODS: 374 Korean subjects were stratified according to the World Health Organization criteria (normal glucose tolerance [NGT], n = 128; impaired glucose tolerance [IGT], n=128; diabetes, n=118) and subdivided further into the two groups; non-obese (BMI < 25 kg/m2) and obese group (BMI 25 kg/m2). Insulinogenic index (the ratio of the increment of insulin to that of plasma glucose 30 min after glucose load) was used as an index of early-phase insulin secretion. AUC insulin (area under the insulin curve during OGTT) was used as an index of total insulin secretion. Insulin resistance was assessed by HOMA (R), the R value of the Homeostasis model. RESULTS: Insulinogenic index decreased significantly in IGT compared with that in NGT in both non-obese and obese groups, respectively. There was no significant difference in AUC insulin and HOMA (R) between NGT and IGT group. WhereasAUC insulin showed its peak level in the range of IGT (7.7~9.9 mmol/L), insulinogenic index showed the peak level in the range of NGT (5.6~7.7 mmol/lL and decreased progressively with increase of plasma glucose 120 min value. CONCLUSION: Early-phase insulin secretory defect might be the initial abnormality in the development of IGT from NGT in both non-obese and obese Korean subjects.
- Distension and Collagenase Digestion Time of The Pancreas are Critical Factors in Islet Isolation of Canine Pancreas.
- Tae Young Yang, In Kyung Jeong, Seung Hoon Oh, Sang Hoon Lee, Dong Jun Kim, Jong Ryul Hahm, Jung Hwan Park, Jong Sung Kim, Jin Soo Han, Sung Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2000;24(2):180-190. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,564 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
S: One of the main problems conditioning the outcome of islet transplantation is the ability to separate a sufficient number of viable islets with preserved function. Islet purification is critically affected by all of the isolation stages, Thus, it is necessary to set up the standard isolation method that islets are separate well from acinar without compromising islet yield and viability. METHODS: Twenty three adult mongrel dogs were used for the experiment of total pancreatectomy with islet isolation. The islets were properly isolated by a modified Recordi method. The obtained islets were further purified by centrifugation on discontinuous gradients using cell separation system (Model 2991, Cobe, Lakewood Colo). We evaluatad islet number (islet equivalent number, 150 gm equivalents/kg of recipient body weight, lEq/kg), purity. cell volume, viabilty, recovery rate, and comparison of outcome according to the isolation conditions. RESULTS: 1) The mean of islet numbers before purification were 13543+/-943 lEq/kg, digestion times were 13.8+/-2.6 min. digestion tamperature was b was 59,7+/-7.0%, viability was 90.0+/-2.1%, cell volume was 4.7+/-1.1 mL, islet number after purification were 4064+/-361 lEq/kg, and recovery rate was 29+2.9. 2) Isolated islet numbers were different according to the degree of pancreas distension with collagenase, digestion temperature, and digestion time. 3) The best conditions for islet isolation were above 37.5 degree C in temperature at recirculation of collagenase, within 12min in digestion time and well distended pancreas with collagenase. 4) According to multiple regression adjusted by variable factors, the degree of pancreas distension with collagenase and digestion time were independently associated factors for successful islet isolation. CONCLUSIONS: In this study, we concluded that the degree of pancreas distension with collagenase and digestion time were independent factors for successful islet isolation and the best conditions for islet isolation were above 37.5 degree C in temperature at recirculation of collagenase, within 12 min in digestion time and well distended pancreas with collagenase.
- Critical Factors Determined Islet Graft Function In Canine Islet Autotransplantation.
- Tae Young Yang, In Kyung Jeong, Seung Hoon Oh, Sang Hoon Lee, Dong Jun Kim, Jong Ryul Hahm, Byung Joon Kim, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sung Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2000;24(2):170-179. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,382 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Islet cell transplantation is an attractive alternative to whole organ pancreas transplantation, since it is clearly safer and simpler surgical procedure for the reciplents. However, several obstacles still remain, because the free islets appear to be more susceptible to non-specific inflammatory damage or immune mediated destruction than islets in an intact pancreas. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to examine the functional outcome of islet autograft and the factors related to the islets graft survival in mongrel dogs. METHODS: Twelve adult mongrel dogs weighting 12~16 kg were used for the experiment of total pancratectomy and islet autotransplantation. The islets were properly isolated by a modified Recordi method. The obtained islets were further purified by centrifugation on discontinuous gradients using cell separation system (Model 2991, Cobe, Lakewood Colo). After the heparization(50U/kg), the islets were injected slowly into the liver through the portal vain for 30 minutes. The post-transplantation intravenous glucose tolerence test (IVGTT) with glucose disappearance rate (K), liver function test (LFT), fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ware measured periodically. RESULTS: I) The median of Ks were 1.3%/min (range 0.3~2.1) and the lEq/kg (150 m equivalents/kg of recipient body weight) was 3520 (range 1350-6550). The Ks in recipients with high lEq/kg (> or =5,000) were significantly higher than those in recipients with low lEq/kg (<5,000)(r=0.78, p<0.05). 2) The islet cell viability were estimated to be 95% and the median of the required insulin dosage for the maintenance of normal FPG were 0.7 (range 0~1.6) U/kg/day, The insulin requirement correlated well with the level of lEq/kg (r=-0.90, p<0.01). 3) The median of the volume of the transplanted pancreatic islet cell were 2.1 mL (range 0.7~5.0) and the purity was 60k (range 10~95), The portal pressure gradients of during the transplant procedure were 4.0(range 0.5~12.0) cmH20. The portal pressure gradients in recipients with high purity were significantly lower than those in recipients with low purity (r=-0,80, p<0,05). CONCLUSIONS: In this study, we confirmed that autotransplantation of islet cell on the pancreatectomized dogs can render nearly normoglycemia, and transplanted islet mass was most critical factor to successful autotransplantation in canine model.
- The Appropriteness of New ADA Diagnostin Criteria for Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Population.
- Moon kyu Lee, Myung Shik Lee, Young Ki Min, Sung Hoon Kim, Byoung Joon Kim, Dong Jun Kim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Eun Young Oh, Yun Jae Chung, Kyoung Ah Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kwang Won Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(3):336-351. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,475 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The ADA has proposed a new diagnostic criteria for diabetes based on fasting plasma glucose, redefining diabetes as fasting plasma glucose 7.0 mmol/L. Since only a few studies for the appropriateness of tbis new ADA criteria were undertaken in the Korean population, we examined the appropriateness of the new ADA criteria by analyzing the results of oral glucose tolerance tests done in our hospital. METHODS: 507 oral glucose tolerance tests were conducted. Cases with diabetes and diseases that could affect the glucose tolerance were excluded. Plasma glucose was measured by the hexokinase method. Three groups of NGT, IGT, and DM by the WHO criteria of 2 hour-plasma glucose were redivided at each level of fasting plasma glucose. We calculated the sensitivity and specificity of each level of fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and the FPG value of maximum accuracy to diagnose diabetes with reference to the WHO criteria of 2 hour-plasma glucose. RESULTS: Correlation between the levels of fasting plasma glucose and 2 hour-plasma glucose was relatively low (r=0.676). FPG of 7.0 mmol/L for diagnosing diabetes was relatively specific (specificity=0.934), but not sensitive (sensitivity= 0.552). FPG value of maximum accuracy for diagnosing diabetes was 6.8 mmol/L. 39 % of IFG (> 6.1mmol/L and < 7.0mmol/L) was reclassified as diabetes by the criteria of 2 hour plasma glucose 11.1 mmol/L and 34 % of NFG (<6.1mmol/L) was reclassified as impaired glucose tolerance by the criteria of 2 hour plasma glucose > 7.8 mmol/L. CONCLUSION: The fasting plasma glucose of 7.0 mmol/L was relatively specific for diagnosing diabetes. However, the new ADA criteria tended to underestimate the prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in the Korean population. Therefore, oral glucose tolerance test may be needed to diagnose diabetes in high risk subjects. Large-scale cross-sectional and prospective studies will be needed to clarify these points.
- Measurement of Anti-Phogrin Antibody in Korean Autoimmune Deabetes; Comparison to Anti-IA-2 Antibody.
- Moon kyu Lee, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Sung Hoon Kim, Byoung Joon Kim, Dong Jun Kim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Dong Kyu Jin, Kyoung Ah Kim, Kwang Won Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(3):269-277. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,282 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Since the discovery of IA-2 as a major autoantigen in type 1 diabetes, the question arose as to whether other PTPs (protein tyrosine phosphatases) could act as diabetic autoantigens as well. A novel PTP, designated IA-2 B (phogrin; phosphatase homologue in granules of insulinoma) was isolated that has a high sequence similarity to IA-2. Since some studies suggested that auto- immunity to phogrin, rather than IA-2 may be more closely associated with the development of type 1 diabetes, we measured the frequency of anti-phogrin antibody in Korean patients with type 1 diabetes and compared it with that of anti-IA-2 antibody/ anti-GAD antibody. METHODS: The anti-phogrin antibody and the anti-IA-2 antibody were measured by radioligand binding assays using in vitro transcribed and translated S-labeled phogrin and IA-2, respectively. Anti-GAD antibody was measured using a commercial radioimmunoassay kit (RSR, Cardiff, U.K.). The subjects in this study consisted of 41 patients with classical type 1 diabetes, 22 with slowly progressive type 1 diabetes, and 39 with type 2 diabetes. Their average mean age was 16.9 years, 37.9 years and 45.3 years respectively. RESULTS: The prevalence of anti-phogrin antibody, anti-IA-2 antibody and anti-GAD antibody in classical type 1 diabetes was 24.4%, 26.8% and 51.2% respectively. That, in slowly progressive type 1 diabetes was 0%, 9.1% and 40.9% respectively. When the anti-GAD antibody assay and the anti-IA-2 antibody assay were combined, the prevalence of autoantibodies was 58.5% in classical type 1 diabetes and 50% in slowly progressive type I diabetes. However, the addition of the anti-phogrin antibody to the anti-GAD antibody/anti-IA-2 antibody measurement did not significantly increase the prevalence of autoantibody. The level of the antiphogrin antibody was positively correlated with that of the anti-IA-2 antibody. The presence of the anti-phogrin antibody and the anti-IA-2 antibody was negatively correlated with the age at diagnosis. One patient with type 1 diabetes had the anti-phogrin antibody without the anti-IA-2 antibody. CONCLUSION: Combined measurement of the anti-phogrin antibody with the anti-IA-2 antibody/ anti-GAD antibody did not significantly increase the prevalence of autoantibodies in Korean patients with type 1 diabetes. In the majority of Korean type 1 diabetes patients, the anti-phogrin antibody appears to share epitopes with the anti-IA-2 antibody. However, a small proportion of type 1 diabetes patients may have a specific autoimmune response to phogrin.
- The Significance of thebeta3 Adrenergic Receptor Gene Polymorphism in Obese Koreans.
- Byoung Joon Kim, Sung Hoon Kim, Dong Jun Kim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Jin Seok Kim, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Jae Hoon Chung, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 1998;22(4):450-456. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,335 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The b3 adrenergic receptor (b3-AR), expressed mainly in visceral fat of human, is involved in regulation of lipolysis and thermogenesis. The missense mutation of b3-AR gene, resulting in the replacement of tryptophan by arginine at position 64 (Trp64Arg), is associated with decreased resting metabolic rate, weight gain and development of obesity. The purpose of this study was to investigate the frequency of the b3-AR gene polymorphism in obese Koreans. Subjects and METHODS: b3-AR genotype was determined in 87 healthy Koreans who visited SMC for the purpose of health checking from Dec/1996 to Feb/1997. Oral glucose tolerance test was performed with 75 g glucose. Lipid profiles, insulin, C-peptide were measured. Anthropometric data was obtained from physical examination and medical records. The subjects with previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus, other endocrine diseases or chronic illness were excluded. To determine the polymorphism, genomic DNA was isolated and PCR and RFLP by MvaI were carried. RESULTS: 1. The difference in frequency of Trp64Arg mutation between two groups was highly significant. (12 subjects (63%) in obese group and 21 subjects (30%) in non obese group, p<0.02) 2. There was significantly high allele frequency in obese group. (obese group: 32 %; non obese group: 15 %, p<0.02). 3. According to BMI, there were significantly high WHR (0.88+0.04 vs 0.83+0.06,p=0.01), total body fat (29.8+7.4 vs 24.4+6.5%, p=0.01) and systolic blood pressure(132+19 vs 124+14mmHg, p=0.04) in obese group. 4. According to b3-AR genotype, there were significantly high WHR (0.830.056 vs. 0.860.05) and 120 min (260.5+171. 5 vs 355.9+234.6 pmol/L, p=0.04) insulin level during OGTT in heterozygote group. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that the frequency of the b3-AR gene mutation was significantly higher in obese Koreans and b3-AR gene polymorphism might play a role in the pathogenesis of obesity.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





